本系列代码托管于:https://github.com/chintsan-code/opencv4-tutorials
本篇使用的项目为:gradient
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char** argv) {
Mat src = imread("../sample/lena512.bmp");
if (src.empty()) {
cout << "could not load image..." << endl;
return -1;
}
namedWindow("input", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("input", src);
// robot gradient 计算
Mat roberts_x = (Mat_<int>(2, 2) << 1, 0, 0, -1);
Mat roberts_y = (Mat_<int>(2, 2) << 0, 1, -1, 0);
Mat grad_x, grad_y;
filter2D(src, grad_x, CV_32F, roberts_x, Point(-1, -1), 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
filter2D(src, grad_y, CV_32F, roberts_y, Point(-1, -1), 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
convertScaleAbs(grad_x, grad_x);
convertScaleAbs(grad_y, grad_y);
Mat roberts_dst;
add(grad_x, grad_y, roberts_dst); //L1
imshow("robot gradient", roberts_dst);
// sobel
Sobel(src, grad_x, CV_32F, 1, 0);
Sobel(src, grad_y, CV_32F, 0, 1);
convertScaleAbs(grad_x, grad_x);
convertScaleAbs(grad_y, grad_y);
Mat sobel_dst;
add(grad_x, grad_y, sobel_dst);
//addWeighted(grad_x, 0.5, grad_y, 0.5, 0, result2);
imshow("sobel gradient", sobel_dst);
// scharr
Scharr(src, grad_x, CV_32F, 1, 0);
Scharr(src, grad_y, CV_32F, 0, 1);
convertScaleAbs(grad_x, grad_x);
convertScaleAbs(grad_y, grad_y);
Mat scharr_dst;
addWeighted(grad_x, 0.5, grad_y, 0.5, 0, scharr_dst);
imshow("scharr gradient", scharr_dst);
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
Roberts算子
属于一阶导数算子。
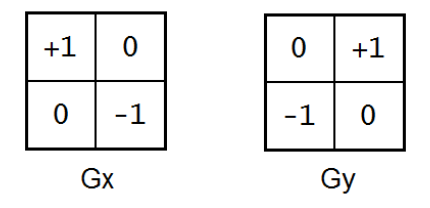
// robot gradient 计算
Mat roberts_x = (Mat_<int>(2, 2) << 1, 0, 0, -1);
Mat roberts_y = (Mat_<int>(2, 2) << 0, 1, -1, 0);
Mat grad_x, grad_y;
filter2D(src, grad_x, CV_32F, roberts_x, Point(-1, -1), 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
filter2D(src, grad_y, CV_32F, roberts_y, Point(-1, -1), 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
convertScaleAbs(grad_x, grad_x);
convertScaleAbs(grad_y, grad_y);
Mat roberts_dst;
add(grad_x, grad_y, roberts_dst); //L1梯度
imshow("robot gradient", roberts_dst);Sobel算子
属于一阶导数算子。

void Sobel( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, int ksize = 3, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT );- src:输入图像
- dst:输出图像。与src具有相同的尺寸和通道数
- ddepth:输出图像的深度。由于卷积核中有负数,一般用CV_32F,如果用CV_8U将会导致导数截断
- dx:x方向的导数阶数
- dy:y方向的导数阶数
- ksize:卷积核尺寸。必须为1,3,5或7
- scale:比例因子,默认为1,即不使用
- delta:在储存目标图像前可选的添加到像素的值,可用于提升亮度。 默认值为0
- borderType:图像边缘处理方式
Scharr算子
属于一阶导数算子。可以看作是Sobel算子的增强
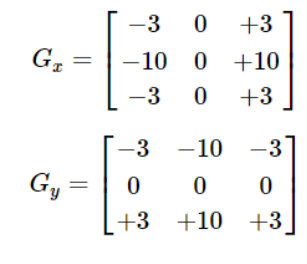
void Scharr( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT );- src:输入图像
- dst:输出图像。与src具有相同的尺寸和通道数
- ddepth:输出图像的深度。由于卷积核中有负数,一般用CV_32F,如果用CV_8U将会导致导数截断
- dx:x方向的导数阶数
- dy:y方向的导数阶数
- scale:比例因子,默认为1,即不使用
- delta:在储存目标图像前可选的添加到像素的值,可用于提升亮度。 默认值为0
- borderType:图像边缘处理方式
一阶导数算子
提取边缘能力:Roberts < Sobel < Scharr
一阶导数最大的地方认为是边缘
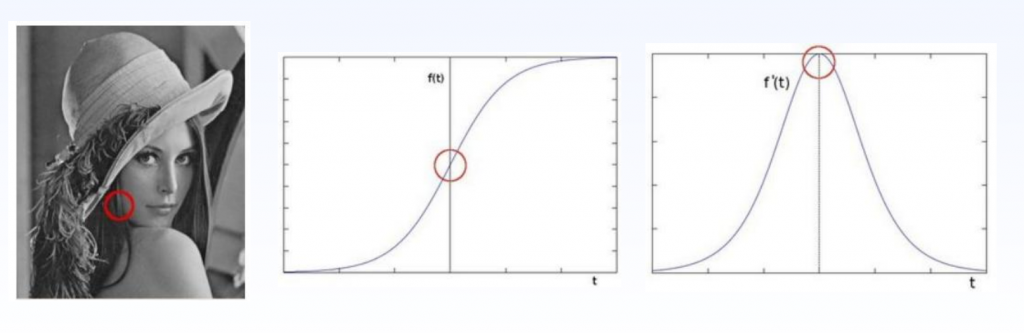
L1梯度
$$G=|G_x|+|G_y|$$
可以用add函数或addWeighted函数实现
L2梯度
$$G=\sqrt{G_x^2+G_y^2}$$










评论 (0)